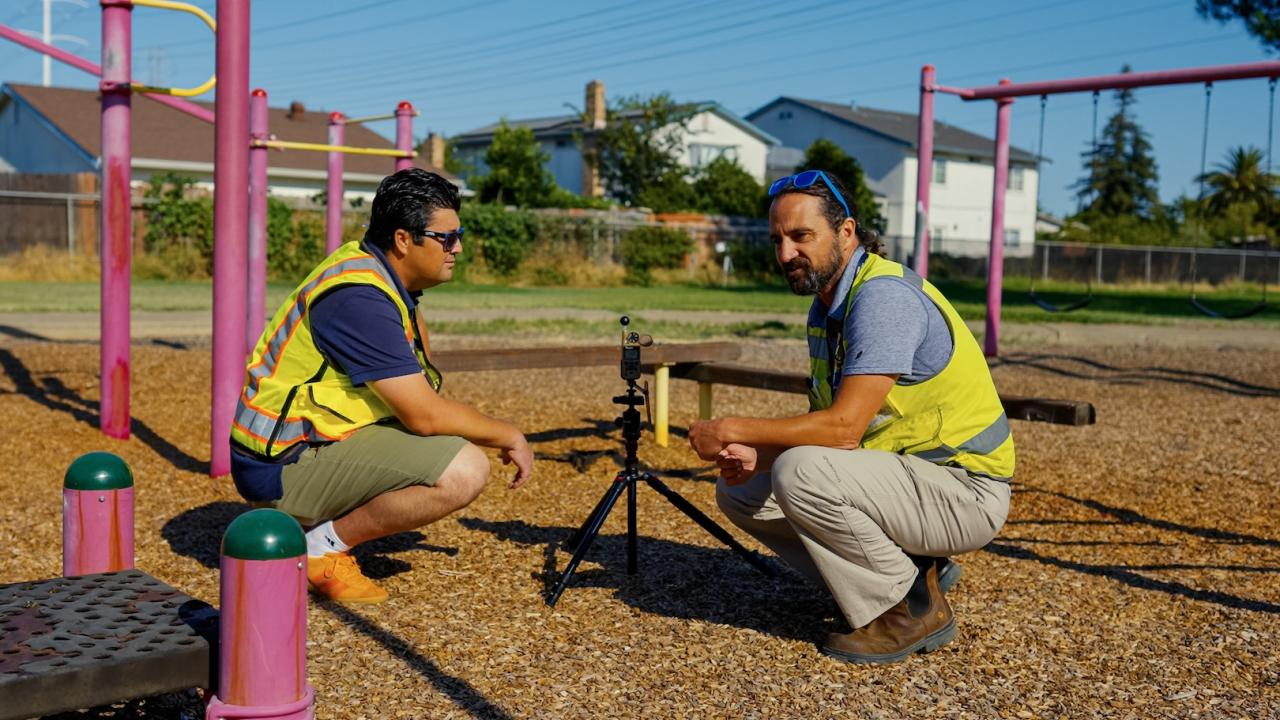
About 85% of elementary schools studied in California experienced some loss of trees between 2018 and 2022, according to a paper from the University of California, Davis, published this month in the journal Urban Forestry and Urban Greening.
Members of the UC Davis Urban Science Lab found that while the average decline was less than 2%, some districts in the Central Valley — including schools with few trees to lose — lost up to a quarter of their tree cover. The most severe losses were concentrated in Tulare County, while the most notable gains were found in Imperial County.
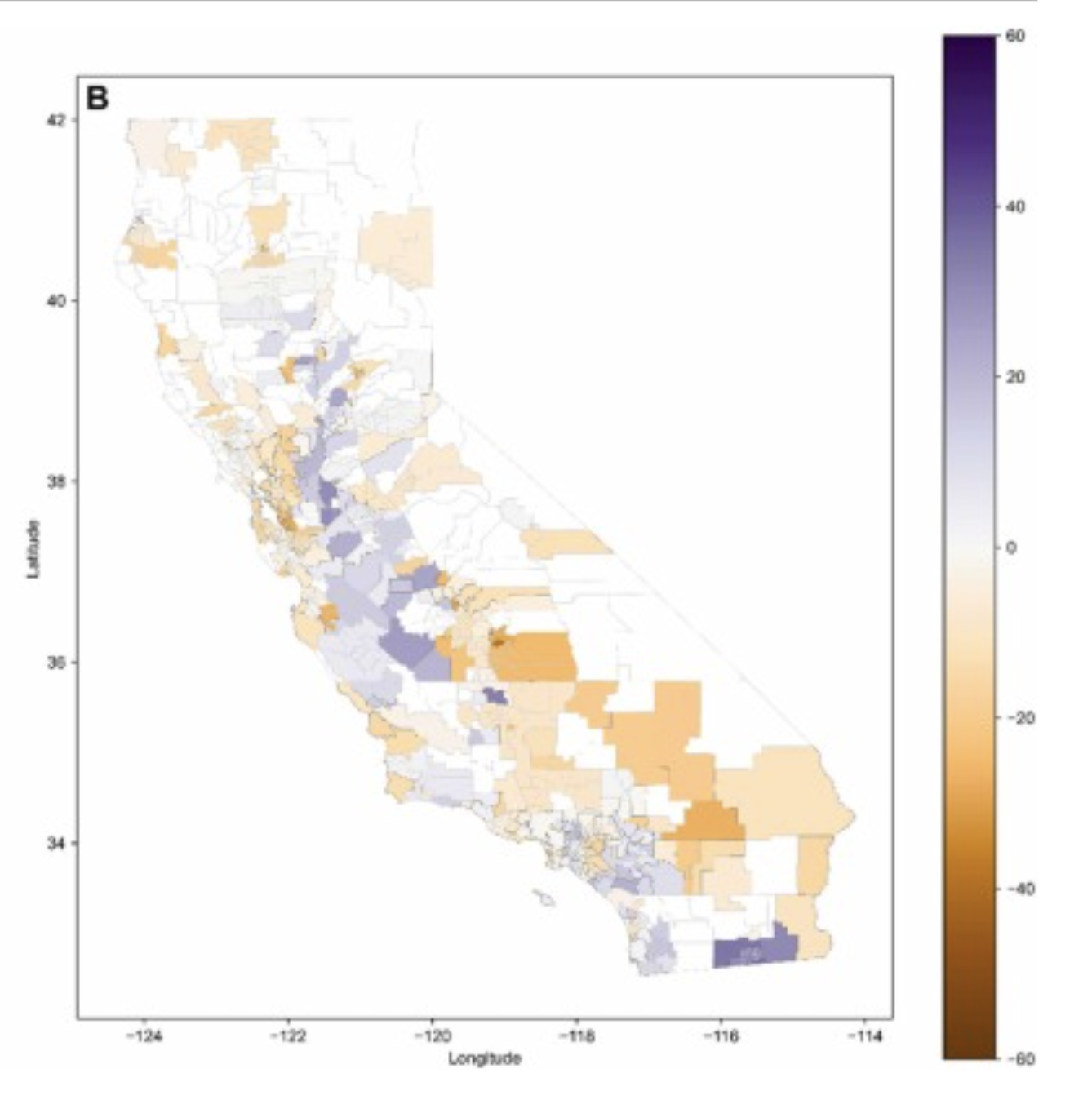
The findings are troubling as climate change will likely intensify extreme heat and drought conditions. The study underscores an urgent need to improve tree canopy in low-shade, high-need schools and to protect existing tree cover in areas facing loss.
“We are trying to measure to what extent we are exposing kids to temperatures that might be stressing their body to a level that becomes uncomfortable or dangerous,” said Alessandro Ossola, an associate professor of plant sciences who directs the Urban Science Lab at UC Davis.
The team continued the research this past summer at elementary schools across the state, measuring tree canopies and maximum temperatures at playgrounds, basketball courts, soccer fields and other outdoor spaces.
Tree canopies cover only about 4% to 6% of the average California school campus. That means the roughly 5.8 million K-12 public school students in California often take breaks and participate in outdoor activities under the glaring sun.
As part of the work, researchers mapped tree cover and heat over the course of a hot day at schools in inland and coastal areas of Northern and Southern California.
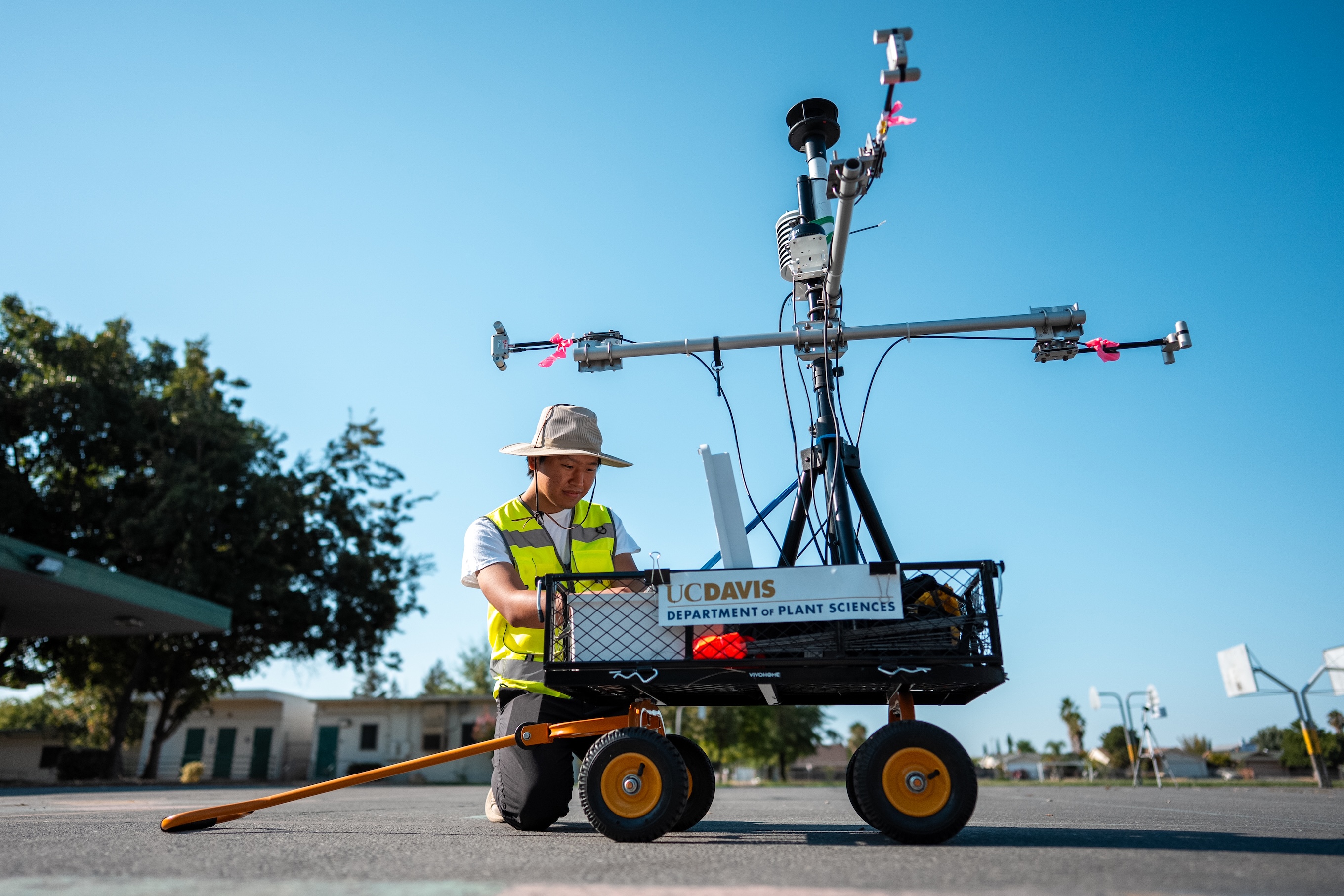

The research is a joint effort with UC Davis, UC Berkeley and UCLA and is funded by the U.S. Forest Service and supported by the nonprofit Green Schoolyards America through its California Schoolyard Tree Canopy study.
“Most schools are actually a nature desert, which is antithetical because we know that early life exposure of humans to nature is critical for them to develop skills, improve their microbiome, become more environmentally active and so on,” Ossola said. “Trees are a hidden asset and an underutilized asset.”
This news release is adapted from a longer article from the UC Davis College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences. Read their full feature story, “Researchers Measure Schoolyard Heat One Step at a Time."
Media Resources
- Alessandro Ossola, Department of Plant Sciences, aossola@ucdavis.edu
- Luisa Velásquez Camacho, Department of Plant Sciences, lfvelasquez@ucdavis.edu
- Kat Kerlin, UC Davis News and Media Relations, 530-750-9195, kekerlin@ucdavis.edu
- Emily C. Dooley, College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, ecdooley@ucdavis.edu
